TF Learn is a simplified interface for TensorFlow, to get people started on predictive analytics and data mining. The library covers a variety of needs: from linear models to Deep Learning applications like text and image understanding.
Install TensorFlow, and then simply import learn via from tensorflow.contrib.learn or use tf.contrib.learn.
Optionally you can install scikit-learn and pandas for additional functionality.
LinearClassifier (docs)LinearRegressor (docs)DNNClassifier (docs)DNNRegressor (docs)DNNLinearCombinedClassifier (docs)DNNLinearCombinedRegressor (docs)SVM (docs)GMM (docs)KMeansClustering (docs)Below are a few simple examples of the API. For more examples, please see examples.
General tips:
It‘s useful to rescale a dataset to 0 mean and unit standard deviation before passing it to an Estimator. Stochastic Gradient Descent doesn’t always do the right thing when variable are at very different scales.
Categorical variables should be managed before passing input to the estimator.
Simple linear classification:
import tensorflow.contrib.learn.python.learn as learn from sklearn import datasets, metrics iris = datasets.load_iris() feature_columns = learn.infer_real_valued_columns_from_input(iris.data) classifier = learn.LinearClassifier(n_classes=3, feature_columns=feature_columns) classifier.fit(iris.data, iris.target, steps=200, batch_size=32) iris_predictions = list(classifier.predict(iris.data, as_iterable=True)) score = metrics.accuracy_score(iris.target, iris_predictions) print("Accuracy: %f" % score)
Simple linear regression:
import tensorflow.contrib.learn.python.learn as learn from sklearn import datasets, metrics, preprocessing boston = datasets.load_boston() x = preprocessing.StandardScaler().fit_transform(boston.data) feature_columns = learn.infer_real_valued_columns_from_input(x) regressor = learn.LinearRegressor(feature_columns=feature_columns) regressor.fit(x, boston.target, steps=200, batch_size=32) boston_predictions = list(regressor.predict(x, as_iterable=True)) score = metrics.mean_squared_error(boston_predictions, boston.target) print ("MSE: %f" % score)
Example of 3 layer network with 10, 20 and 10 hidden units respectively:
import tensorflow.contrib.learn.python.learn as learn from sklearn import datasets, metrics iris = datasets.load_iris() feature_columns = learn.infer_real_valued_columns_from_input(iris.data) classifier = learn.DNNClassifier(hidden_units=[10, 20, 10], n_classes=3, feature_columns=feature_columns) classifier.fit(iris.data, iris.target, steps=200, batch_size=32) iris_predictions = list(classifier.predict(iris.data, as_iterable=True)) score = metrics.accuracy_score(iris.target, iris_predictions) print("Accuracy: %f" % score)
Example of how to pass a custom model to the Estimator:
from sklearn import datasets from sklearn import metrics import tensorflow as tf import tensorflow.contrib.layers.python.layers as layers import tensorflow.contrib.learn.python.learn as learn iris = datasets.load_iris() def my_model(features, labels): """DNN with three hidden layers.""" # Convert the labels to a one-hot tensor of shape (length of features, 3) and # with a on-value of 1 for each one-hot vector of length 3. labels = tf.one_hot(labels, 3, 1, 0) # Create three fully connected layers respectively of size 10, 20, and 10. features = layers.stack(features, layers.fully_connected, [10, 20, 10]) # Create two tensors respectively for prediction and loss. prediction, loss = ( tf.contrib.learn.models.logistic_regression(features, labels) ) # Create a tensor for training op. train_op = tf.contrib.layers.optimize_loss( loss, tf.contrib.framework.get_global_step(), optimizer='Adagrad', learning_rate=0.1) return {'class': tf.argmax(prediction, 1), 'prob': prediction}, loss, train_op classifier = learn.Estimator(model_fn=my_model) classifier.fit(iris.data, iris.target, steps=1000) y_predicted = [ p['class'] for p in classifier.predict(iris.data, as_iterable=True)] score = metrics.accuracy_score(iris.target, y_predicted) print('Accuracy: {0:f}'.format(score))
Each estimator supports a model_dir argument, which takes a folder path where all model information will be saved:
classifier = learn.DNNClassifier(..., model_dir="/tmp/my_model")
If you run multiple fit operations on the same Estimator, training will resume where the last operation left off, e.g.:
To restore checkpoints to a new Estimator, just pass it the same model_dir argument, e.g.:
If you supply a model_dir argument to your Estimators, TensorFlow will write summaries for loss and histograms for variables in this directory. (You can also add custom summaries in your custom model function by calling Summary operations.)
To view the summaries in TensorBoard, run the following command, where logdir is the model_dir for your Estimator:
tensorboard --logdir=/tmp/tf_examples/my_model_1
and then load the reported URL.
Graph visualization
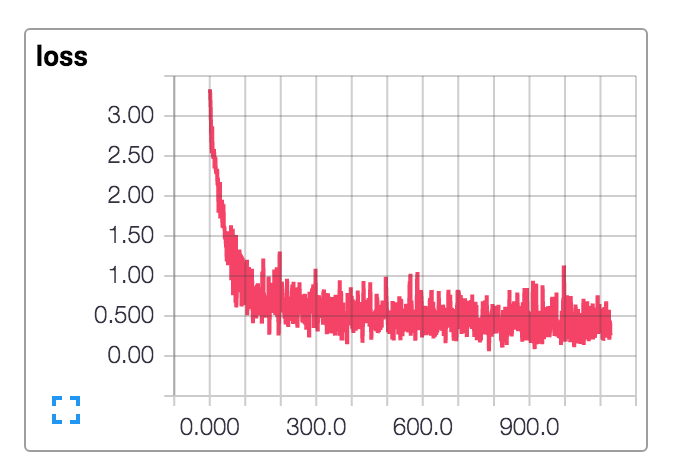
Loss visualization
See the examples folder for: